Cancers, Free Full-Text
Por um escritor misterioso
Last updated 19 setembro 2024
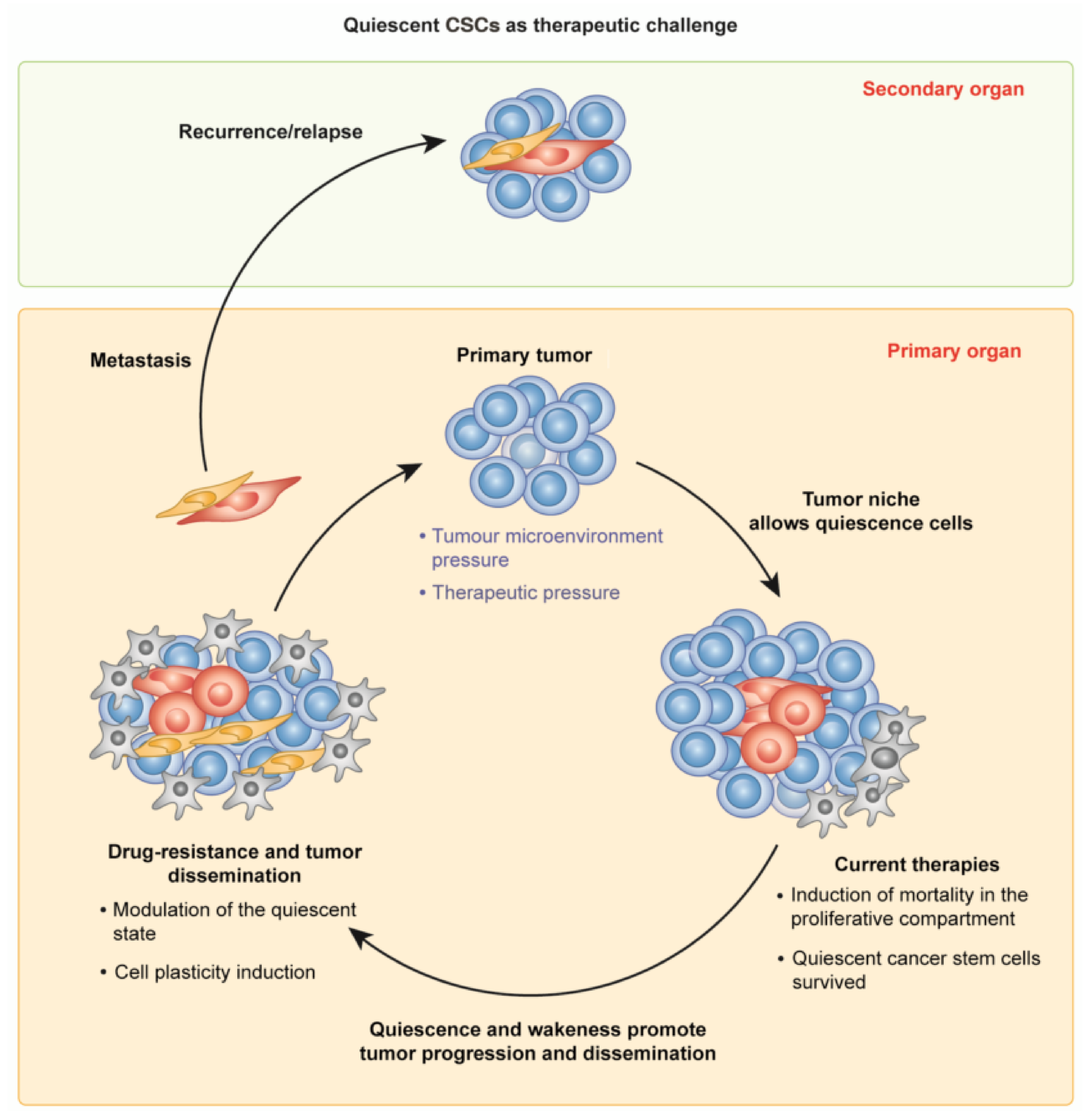
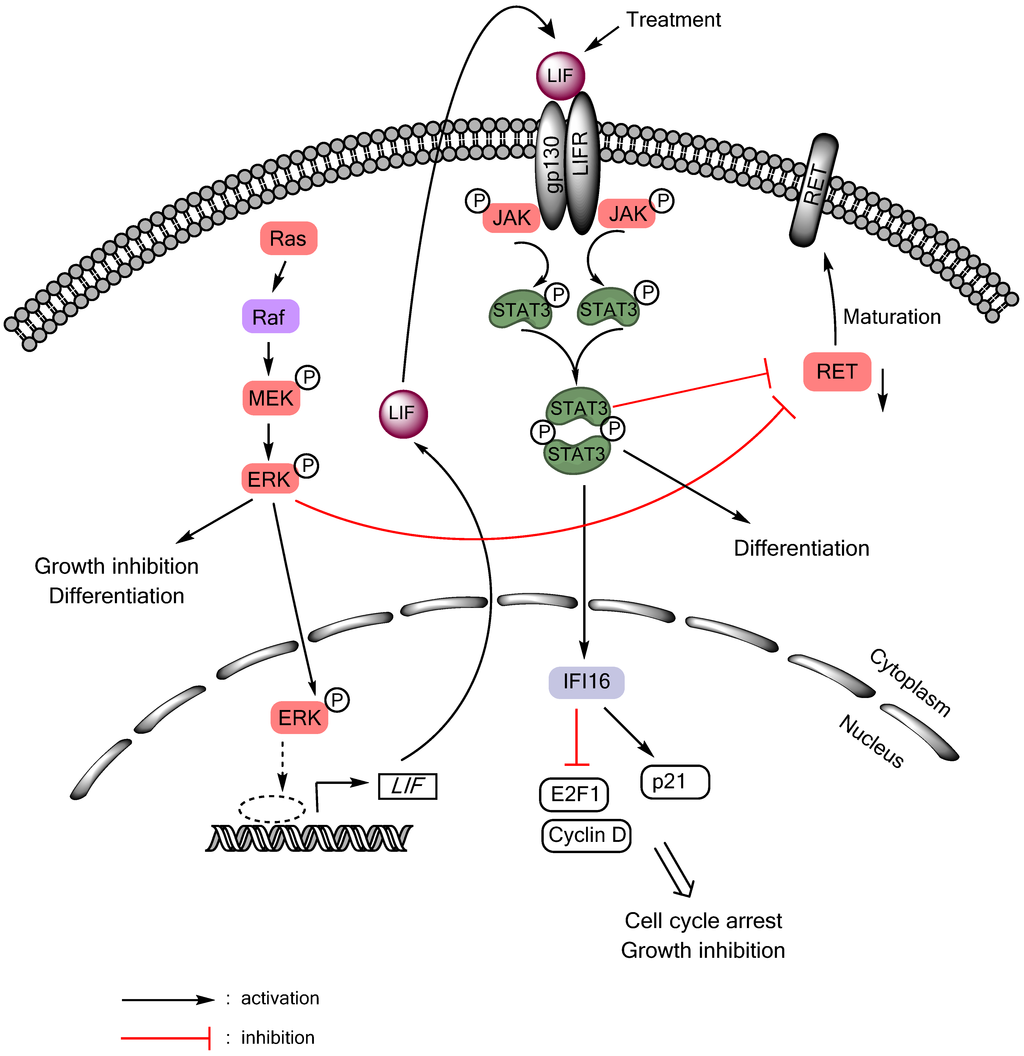
Emerging evidence suggests that a small subpopulation of cancer stem cells (CSCs) is responsible for initiation, progression, and metastasis cascade in tumors. CSCs share characteristics with normal stem cells, i.e., self-renewal and differentiation potential, suggesting that they can drive cancer progression. Consequently, targeting CSCs to prevent tumor growth or regrowth might offer a chance to lead the fight against cancer. CSCs create their niche, a specific area within tissue with a unique microenvironment that sustains their vital functions. Interactions between CSCs and their niches play a critical role in regulating CSCs’ self-renewal and tumorigenesis. Differences observed in the frequency of CSCs, due to the phenotypic plasticity of many cancer cells, remain a challenge in cancer therapeutics, since CSCs can modulate their transcriptional activities into a more stem-like state to protect themselves from destruction. This plasticity represents an essential step for future therapeutic approaches. Regarding self-renewal, CSCs are modulated by the same molecular pathways found in normal stem cells, such as Wnt/β-catenin signaling, Notch signaling, and Hedgehog signaling. Another key characteristic of CSCs is their resistance to standard chemotherapy and radiotherapy treatments, due to their capacity to rest in a quiescent state. This review will analyze the primary mechanisms involved in CSC tumorigenesis, with particular attention to the roles of CSCs in tumor progression in benign and malignant diseases; and will examine future perspectives on the identification of new markers to better control tumorigenesis, as well as dissecting the metastasis process.
Cancers, Free Full-Text
Prostate Cancer: Symptoms, Causes & Treatment
Detection of HPV-16 DNA by PCR in histologically cancer free lymph nodes from patients with cervical cancer. - Abstract - Europe PMC

Pembrolizumab as Second-Line Therapy for Advanced Urothelial Carcinoma

HER2 and Response to Paclitaxel in Node-Positive Breast Cancer
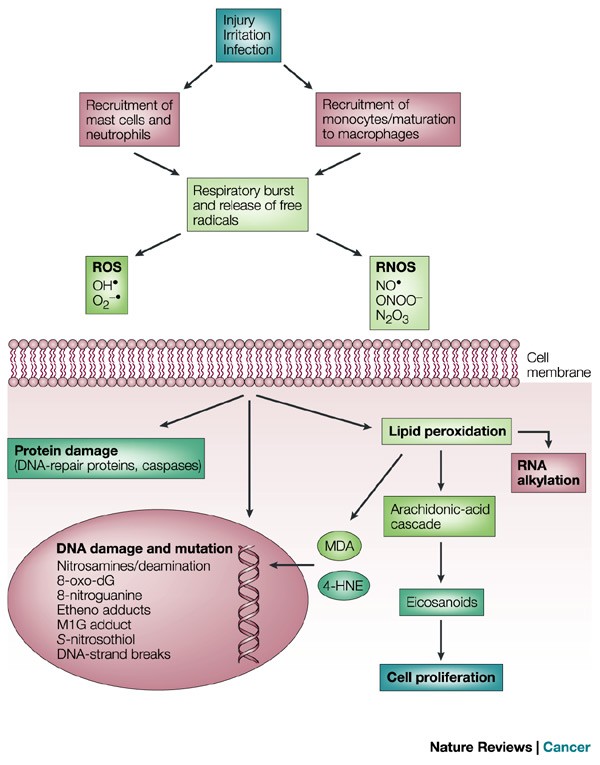
Radical causes of cancer
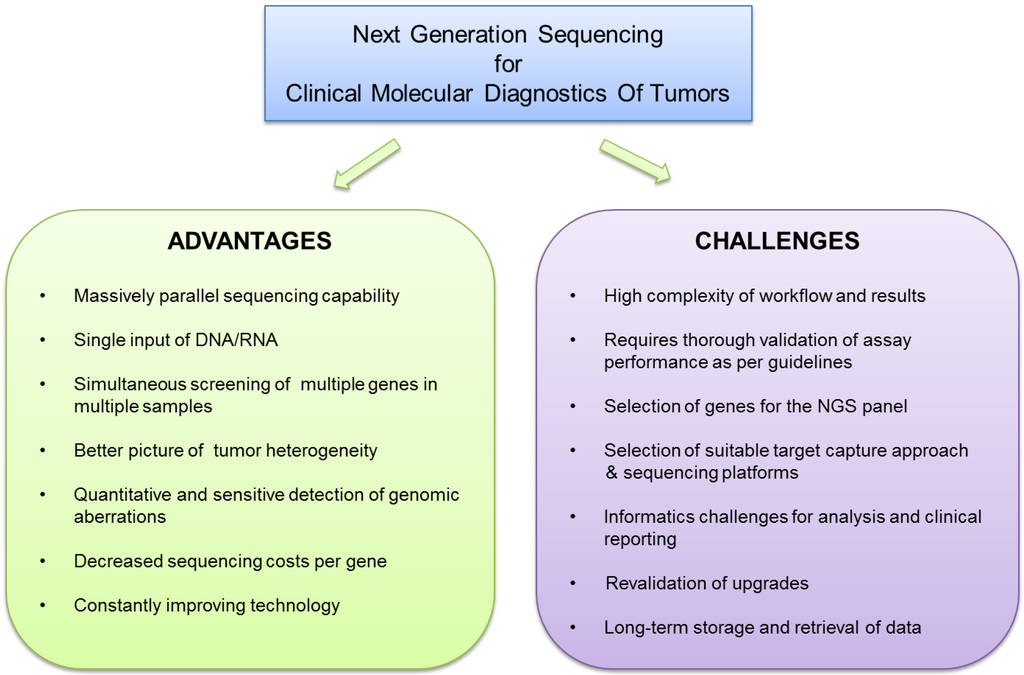
Cancers, Free Full-Text

Cancer Metastasis: Building a Framework: Cell

Neoadjuvant Nivolumab plus Chemotherapy in Resectable Lung Cancer
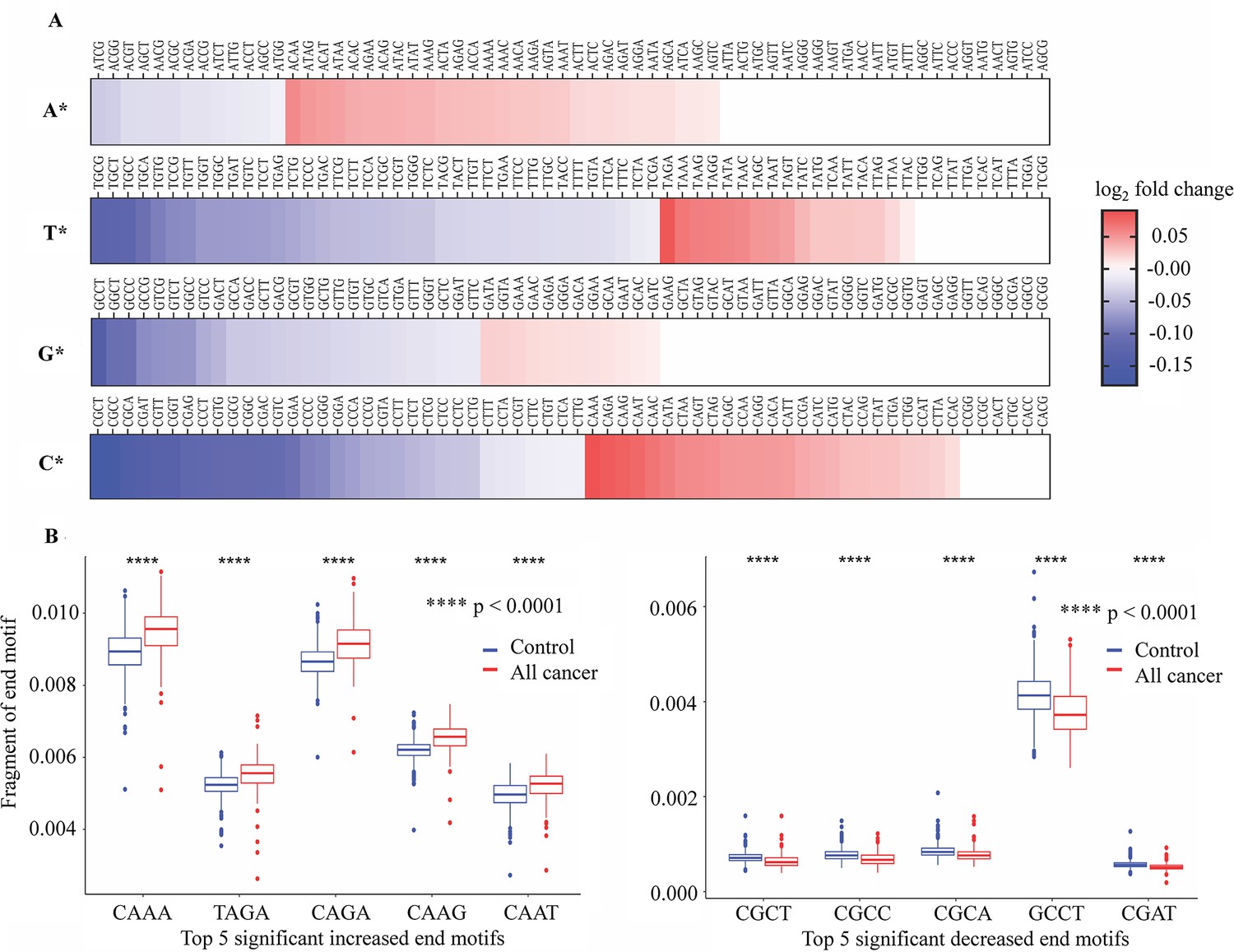
Multimodal analysis of methylomics and fragmentomics in plasma cell-free DNA for multi-cancer early detection and localization
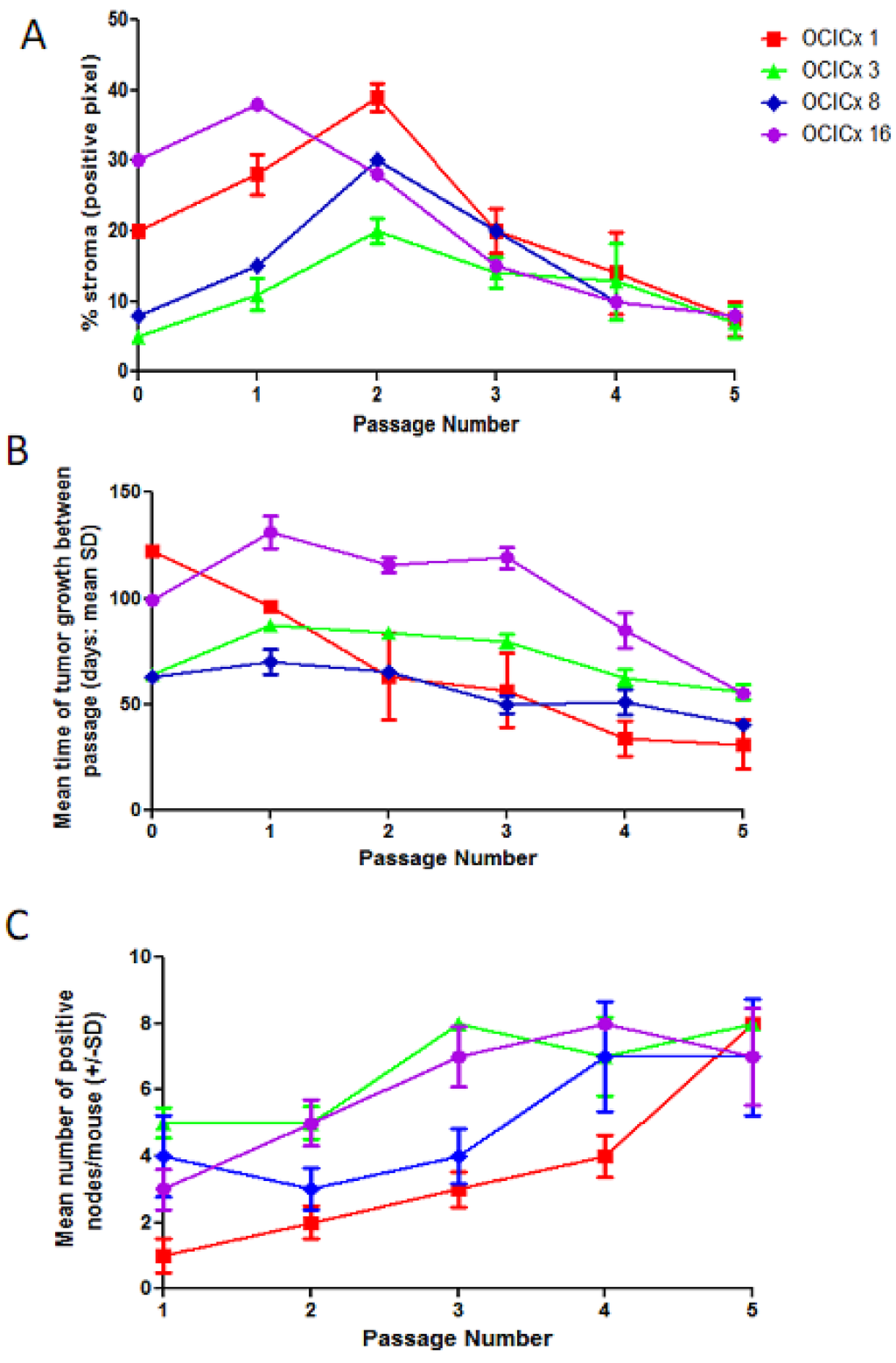
Cancers, Free Full-Text
Recomendado para você
-
 The Hana Hana no Mi (Devil Fruit Encyclopedia)19 setembro 2024
The Hana Hana no Mi (Devil Fruit Encyclopedia)19 setembro 2024 -
 Interior Design Spring Market Tabloid 2023 by Interior Design Magazine - Issuu19 setembro 2024
Interior Design Spring Market Tabloid 2023 by Interior Design Magazine - Issuu19 setembro 2024 -
 Ushi Ushi no Mi, Model: Giraffe, One Piece Wiki19 setembro 2024
Ushi Ushi no Mi, Model: Giraffe, One Piece Wiki19 setembro 2024 -
 Awakened Hana Hana no mi : r/MemePiece19 setembro 2024
Awakened Hana Hana no mi : r/MemePiece19 setembro 2024 -
 Nico Robin by Shin23J on DeviantArt19 setembro 2024
Nico Robin by Shin23J on DeviantArt19 setembro 2024 -
 If you could create a new fighting style in the One Piece universe, what would your idea be? : r/MemePiece19 setembro 2024
If you could create a new fighting style in the One Piece universe, what would your idea be? : r/MemePiece19 setembro 2024 -
 Strongest Straw Hat Pirates, Ranked19 setembro 2024
Strongest Straw Hat Pirates, Ranked19 setembro 2024 -
 Baraaaa on X: Hana Hana No Mi mode Awakening kah?? Sugooiiii19 setembro 2024
Baraaaa on X: Hana Hana No Mi mode Awakening kah?? Sugooiiii19 setembro 2024 -
 Flint Repertory Theatre set to debut 'The Magnificent Seven19 setembro 2024
Flint Repertory Theatre set to debut 'The Magnificent Seven19 setembro 2024 -
 Hanahana-no Mi and Ope-ope-no Mi are now available as cakes19 setembro 2024
Hanahana-no Mi and Ope-ope-no Mi are now available as cakes19 setembro 2024
você pode gostar
-
Gol bolinha modificado19 setembro 2024
-
 Roblox is an Online Game Platform and Game Creation System. it Allows Users To Program Games and Play Games Created by Other Users Editorial Stock Image - Image of background, cellphone: 21455992919 setembro 2024
Roblox is an Online Game Platform and Game Creation System. it Allows Users To Program Games and Play Games Created by Other Users Editorial Stock Image - Image of background, cellphone: 21455992919 setembro 2024 -
 Warriors - Manga/Graphic Novels : Erin Hunter : Free Download, Borrow, and Streaming : Internet Archive19 setembro 2024
Warriors - Manga/Graphic Novels : Erin Hunter : Free Download, Borrow, and Streaming : Internet Archive19 setembro 2024 -
 Top memes de Floppa en español :) Memedroid19 setembro 2024
Top memes de Floppa en español :) Memedroid19 setembro 2024 -
 The Backrooms Found Footage - Part 1 :The+Poolrooms:19 setembro 2024
The Backrooms Found Footage - Part 1 :The+Poolrooms:19 setembro 2024 -
 Watch us play the utterly unhinged but maybe possibly brilliant My Summer Car19 setembro 2024
Watch us play the utterly unhinged but maybe possibly brilliant My Summer Car19 setembro 2024 -
 Estelí logra la proeza y está en la final de la Copa de Campeones19 setembro 2024
Estelí logra la proeza y está en la final de la Copa de Campeones19 setembro 2024 -
 Best Arena 9 Decks cool deck, arena, clash royale19 setembro 2024
Best Arena 9 Decks cool deck, arena, clash royale19 setembro 2024 -
 Neil Druckmann of Naughty Dog refused to comment on The Last of Us – Part III and the multiplayer game, but confirmed “other projects” : r/thelastofusfactions19 setembro 2024
Neil Druckmann of Naughty Dog refused to comment on The Last of Us – Part III and the multiplayer game, but confirmed “other projects” : r/thelastofusfactions19 setembro 2024 -
 Novo preço mínimo para a saca de café conilon robusta de Rondônia durante a safra de 2021/22 é estabelecido19 setembro 2024
Novo preço mínimo para a saca de café conilon robusta de Rondônia durante a safra de 2021/22 é estabelecido19 setembro 2024
