Fiber deprivation and microbiome-borne curli shift gut bacterial populations and accelerate disease in a mouse model of Parkinson's disease - ScienceDirect
Por um escritor misterioso
Last updated 20 março 2025

Parkinson’s disease (PD) is a neurological disorder characterized by motor dysfunction, dopaminergic neuron loss, and alpha-synuclein (αSyn) inclusion…

Dietary fibre deprivation and bacterial curli exposure shift gut microbiome and exacerbate Parkinson's disease-like pathologies in an alpha-synuclein-overexpressing mouse

Fiber deprivation and microbiome-borne curli shift gut bacterial populations and accelerate disease in a mouse model of Parkinson's disease - ScienceDirect

Gut Microbiota Regulate Motor Deficits and Neuroinflammation in a Model of Parkinson's Disease - ScienceDirect
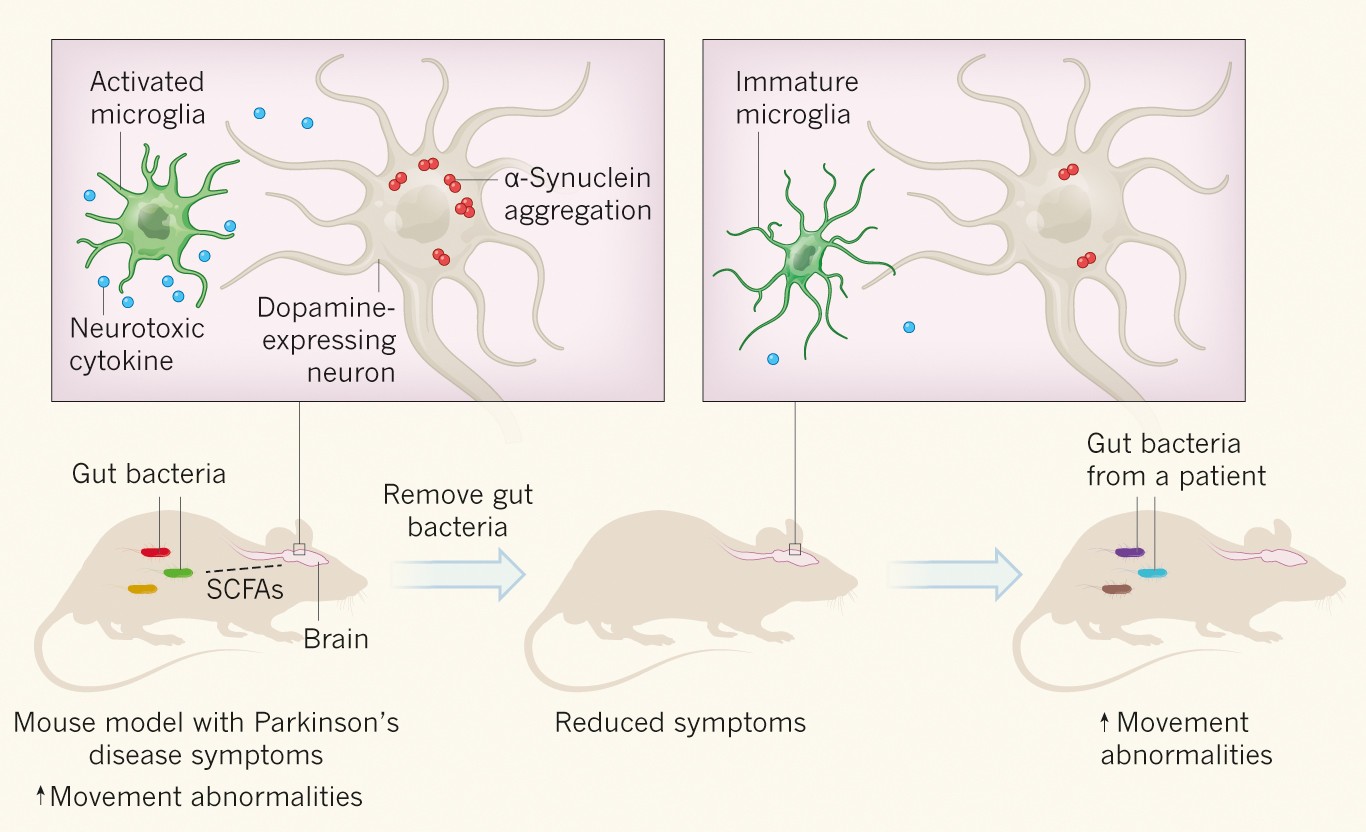
Gut microbes augment neurodegeneration

Dietary fibre deprivation and bacterial curli exposure shift gut microbiome and exacerbate Parkinson's disease-like pathologies in an alpha-synuclein-overexpressing mouse

Dietary fibre deprivation and bacterial curli exposure shift gut microbiome and exacerbate Parkinson's disease-like pathologies in an alpha-synuclein-overexpressing mouse

The gut microbiome in neurological disorders - The Lancet Neurology

Parkinson's disease: Are gut microbes involved? American Journal of Physiology-Gastrointestinal and Liver Physiology

Implications of the Human Gut–Brain and Gut–Cancer Axes for Future Nanomedicine
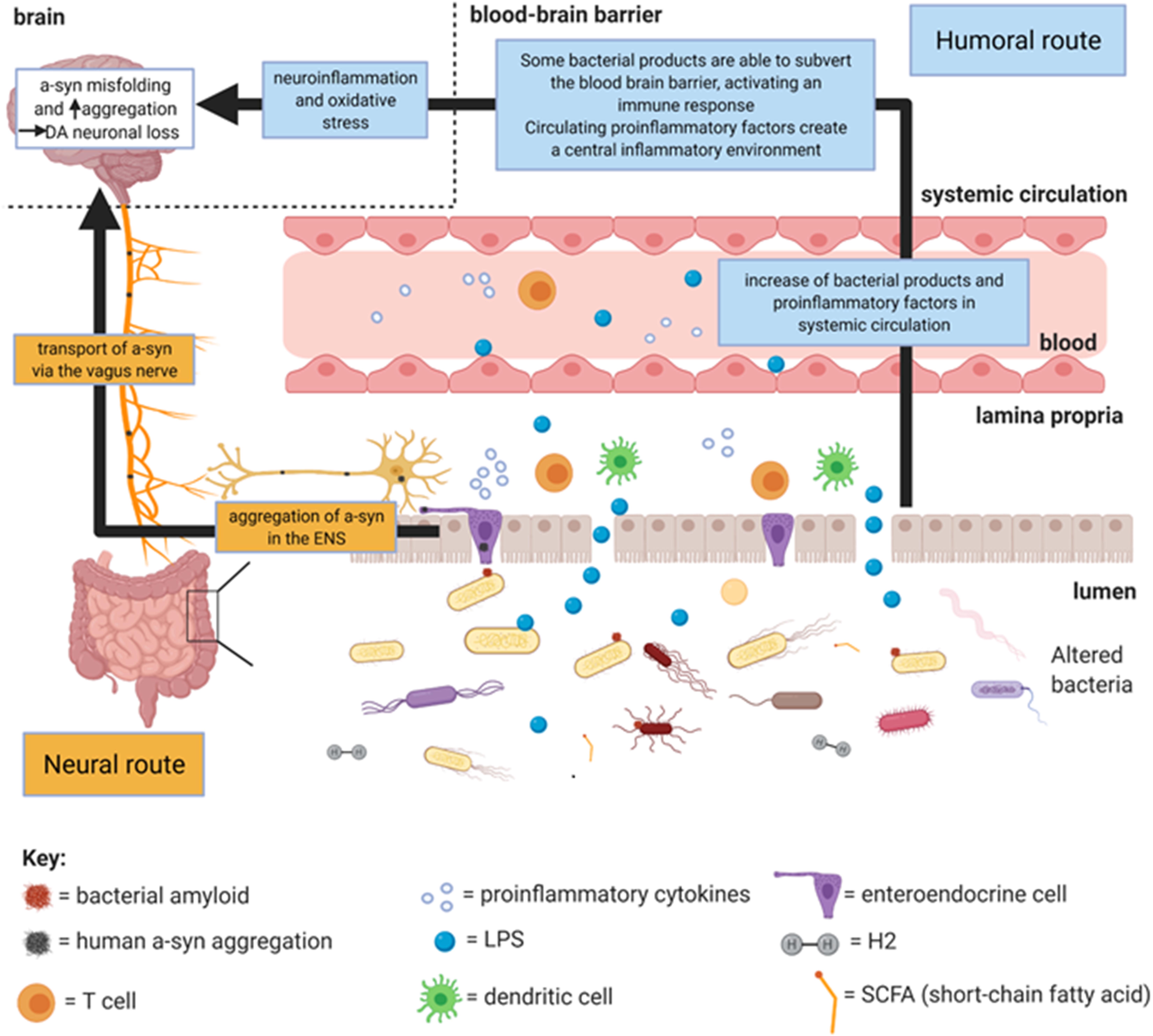
Frontiers What Is Our Understanding of the Influence of Gut Microbiota on the Pathophysiology of Parkinson's Disease?
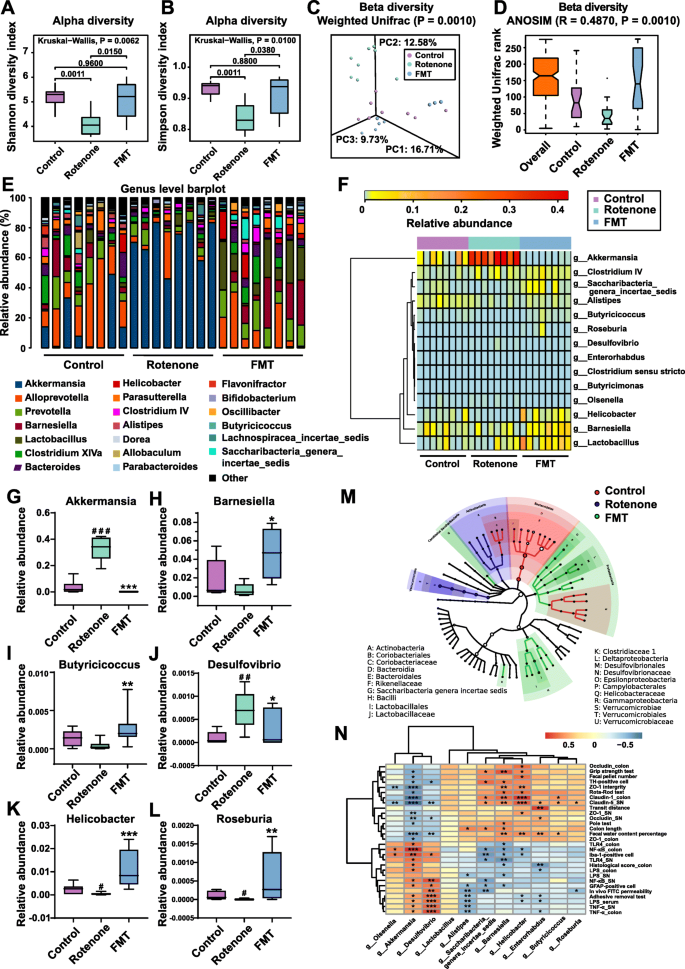
Fecal microbiota transplantation protects rotenone-induced Parkinson's disease mice via suppressing inflammation mediated by the lipopolysaccharide-TLR4 signaling pathway through the microbiota-gut-brain axis, Microbiome
Recomendado para você
-
 Desapego Games - GTA > GTA 5 ONLINE FIVEM GTA RP GRAND THEFT AUTO20 março 2025
Desapego Games - GTA > GTA 5 ONLINE FIVEM GTA RP GRAND THEFT AUTO20 março 2025 -
Duda Games|Pesquisa do TikTok20 março 2025
-
 duda games gta rp20 março 2025
duda games gta rp20 março 2025 -
 Petition · To add Roleplay in GTA V for PS4 and XBOX ·20 março 2025
Petition · To add Roleplay in GTA V for PS4 and XBOX ·20 março 2025 -
 ENCONTREI A DUDA NO ROLEPLAY MOBILE - SÓ OS GADOS - One State RP20 março 2025
ENCONTREI A DUDA NO ROLEPLAY MOBILE - SÓ OS GADOS - One State RP20 março 2025 -
 CONHECI A DISNEY? UM PARQUE DE DIVERSÃO!! GTARP12 #JUJUBA20 março 2025
CONHECI A DISNEY? UM PARQUE DE DIVERSÃO!! GTARP12 #JUJUBA20 março 2025 -
 Winter 2020 Back to School Print Edition, Arts & Entertainment20 março 2025
Winter 2020 Back to School Print Edition, Arts & Entertainment20 março 2025 -
 Desapego Games - Genshin Impact > CONTA AR57, COM 14 PERSONAGENS 5* (3 ARCONTES INCLUSOS) E 10 ARMAS 5* ESTRELAS20 março 2025
Desapego Games - Genshin Impact > CONTA AR57, COM 14 PERSONAGENS 5* (3 ARCONTES INCLUSOS) E 10 ARMAS 5* ESTRELAS20 março 2025 -
 Tetiana Gaidar, Resident Evil Wiki20 março 2025
Tetiana Gaidar, Resident Evil Wiki20 março 2025 -
 Saturday Afternoon Picnic with Kristy Caldwell – Peachtree Publishing Company Inc.20 março 2025
Saturday Afternoon Picnic with Kristy Caldwell – Peachtree Publishing Company Inc.20 março 2025
você pode gostar
-
 T-shirt Hope Colorido Coração Bordado - Use Criativa - Camiseta Feminina - Magazine Luiza20 março 2025
T-shirt Hope Colorido Coração Bordado - Use Criativa - Camiseta Feminina - Magazine Luiza20 março 2025 -
 Banner Festa Halloween Grupo Morcegos Papel Estilo Bonito Isolado Png imagem vetorial de Phiradet.c© 42082683820 março 2025
Banner Festa Halloween Grupo Morcegos Papel Estilo Bonito Isolado Png imagem vetorial de Phiradet.c© 42082683820 março 2025 -
 five nights at freddy's™ frostbear plush 8in, Five Below20 março 2025
five nights at freddy's™ frostbear plush 8in, Five Below20 março 2025 -
 IT'S GOOD, ACTUALLY / Sunset Park / Michael Dean Clark I Drunk Monkeys20 março 2025
IT'S GOOD, ACTUALLY / Sunset Park / Michael Dean Clark I Drunk Monkeys20 março 2025 -
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/most-common-chess-openings-611517-English-Opening-764225097663401da4c27871ae3da62e.jpg) Common Chess Openings You Should Learn20 março 2025
Common Chess Openings You Should Learn20 março 2025 -
 Que Pro La Historia Detrás del Meme20 março 2025
Que Pro La Historia Detrás del Meme20 março 2025 -
 Bocchi the Rock! – Wikipedia tiếng Việt20 março 2025
Bocchi the Rock! – Wikipedia tiếng Việt20 março 2025 -
 GABINETE GAMEMAX H602-WB 1 FAN VERDE - Styletec20 março 2025
GABINETE GAMEMAX H602-WB 1 FAN VERDE - Styletec20 março 2025 -
 Vetores de Ícone Do Jogo Do Dedo Do Pé Do Tic Tac No Fundo Branco20 março 2025
Vetores de Ícone Do Jogo Do Dedo Do Pé Do Tic Tac No Fundo Branco20 março 2025 -
 Money Easily é confiável? Confira nossa análise em 202320 março 2025
Money Easily é confiável? Confira nossa análise em 202320 março 2025
