Metabolite Toxicity as a Driver of Aging and Disease — THE HUGHES LAB
Por um escritor misterioso
Last updated 20 setembro 2024
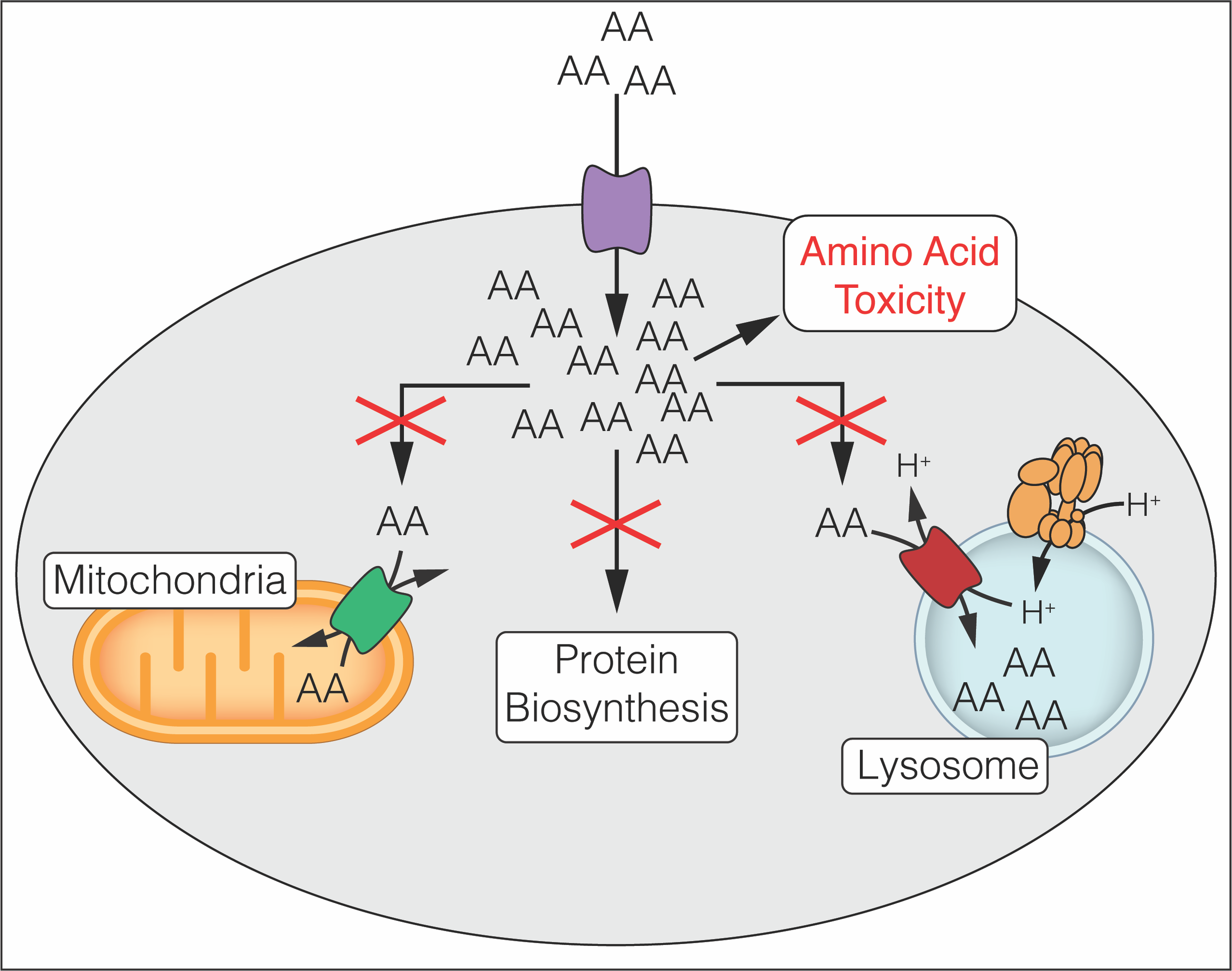
Metabolite Toxicity as a Driver of Aging and Disease

Mitochondrial-derived compartments facilitate cellular adaptation to amino acid stress - ScienceDirect

Adipaging': ageing and obesity share biological hallmarks related to a dysfunctional adipose tissue - Pérez - 2016 - The Journal of Physiology - Wiley Online Library
Research Overview — THE HUGHES LAB

The Path to Progress Preclinical Studies of Age-Related Neurodegenerative Diseases: A Perspective on Rodent and hiPSC-Derived Models - ScienceDirect

Toxicity of Tetrabromobisphenol A and Its Derivative in the Mouse Liver Following Oral Exposure at Environmentally Relevant Levels

How Reactive Metabolites Induce an Immune Response That Sometimes Leads to an Idiosyncratic Drug Reaction
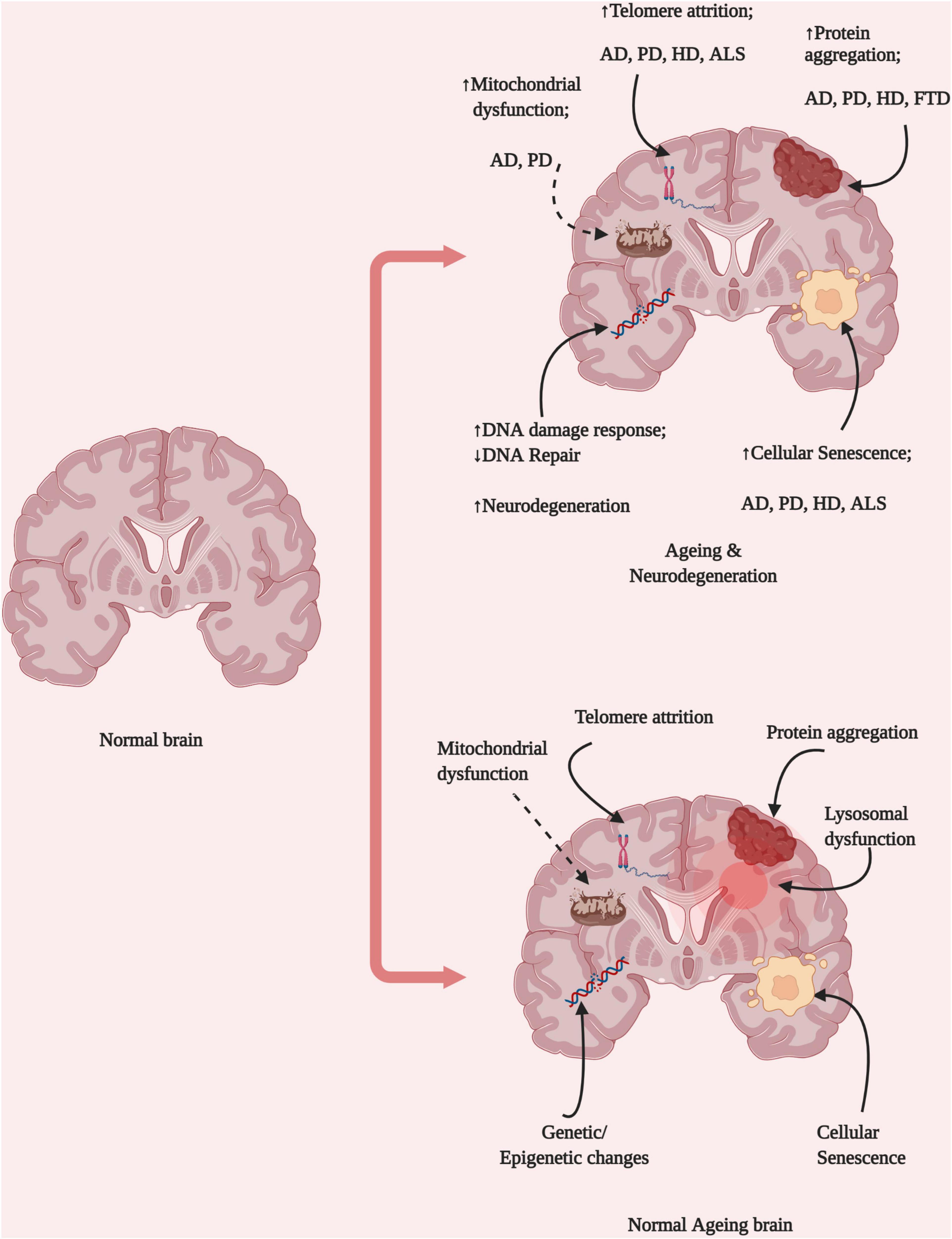
Frontiers The Ageing Brain: Molecular and Cellular Basis of Neurodegeneration
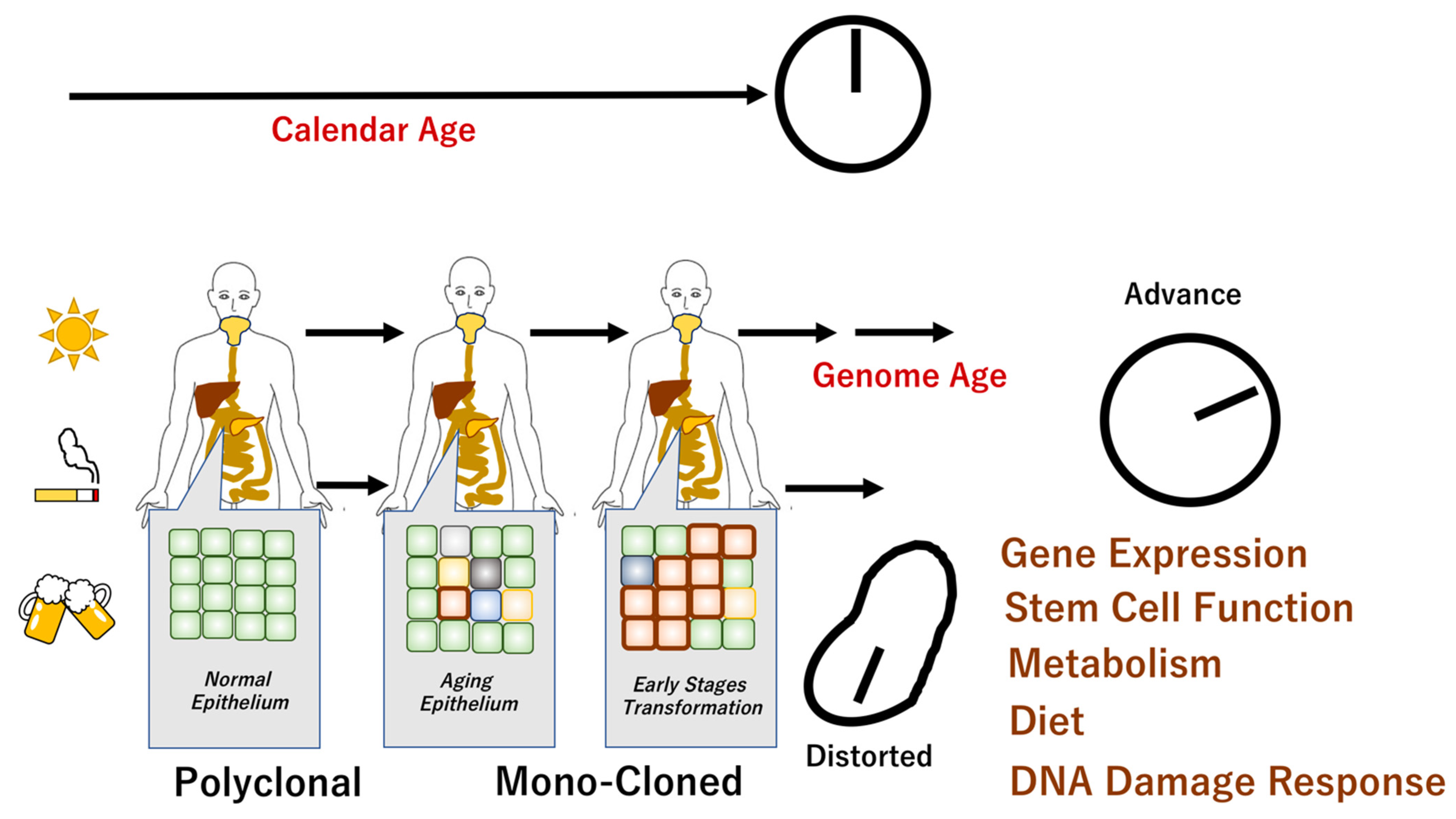
IJMS, Free Full-Text

Structural Alert/Reactive Metabolite Concept as Applied in Medicinal Chemistry to Mitigate the Risk of Idiosyncratic Drug Toxicity: A Perspective Based on the Critical Examination of Trends in the Top 200 Drugs Marketed
Recomendado para você
-
 Toxicity LP20 setembro 2024
Toxicity LP20 setembro 2024 -
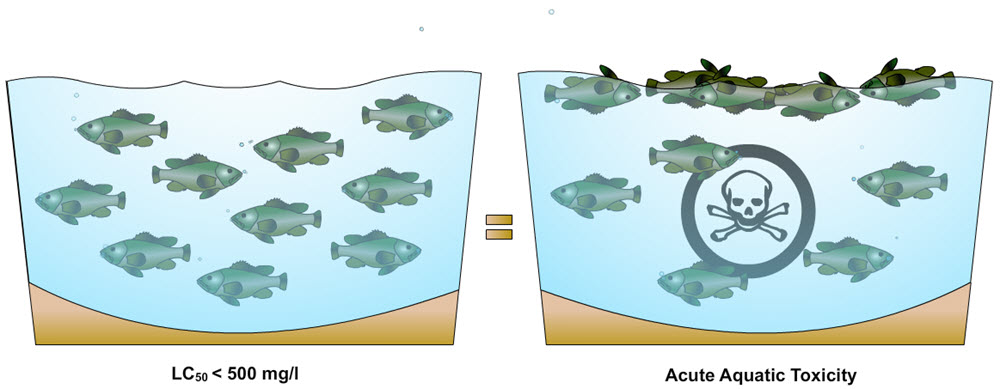 Acute Aquatic Toxicity Department of Toxic Substances Control20 setembro 2024
Acute Aquatic Toxicity Department of Toxic Substances Control20 setembro 2024 -
 System Of A Down – Toxicity Lyrics20 setembro 2024
System Of A Down – Toxicity Lyrics20 setembro 2024 -
 System of a Down - Toxicity Poster 36 x 24 - The Blacklight Zone20 setembro 2024
System of a Down - Toxicity Poster 36 x 24 - The Blacklight Zone20 setembro 2024 -
 Toxicity and Antidotes20 setembro 2024
Toxicity and Antidotes20 setembro 2024 -
 Set sign biohazard toxicity dangerous yellow signs20 setembro 2024
Set sign biohazard toxicity dangerous yellow signs20 setembro 2024 -
 System Of A Down - Toxicity - Music20 setembro 2024
System Of A Down - Toxicity - Music20 setembro 2024 -
 Measures of Toxicity20 setembro 2024
Measures of Toxicity20 setembro 2024 -
 Vitamin D Toxicity - Symptoms, Diagnosis, Treatment : Dr. Zaidi20 setembro 2024
Vitamin D Toxicity - Symptoms, Diagnosis, Treatment : Dr. Zaidi20 setembro 2024 -
 Toxicity (2019) - IMDb20 setembro 2024
Toxicity (2019) - IMDb20 setembro 2024
você pode gostar
-
 Jogo 4 Copos Americano Old Fashion Vidro 315ml Nadir Bartender Store - Seu Portal de Produtos para Bar20 setembro 2024
Jogo 4 Copos Americano Old Fashion Vidro 315ml Nadir Bartender Store - Seu Portal de Produtos para Bar20 setembro 2024 -
 Pokemon Trading Card Game coming - Apps - What Mobile20 setembro 2024
Pokemon Trading Card Game coming - Apps - What Mobile20 setembro 2024 -
Jojo pose!!! @aizensgf severing as Kira from JJBA . . . We are official partners with @nerds_with_melanin, @urbananimelounge and a member…20 setembro 2024
-
 Tengoku Daimakyou - Dublado – Episódio 13 Online - Hinata Soul20 setembro 2024
Tengoku Daimakyou - Dublado – Episódio 13 Online - Hinata Soul20 setembro 2024 -
 Croácia e escócia na fase de grupos. ilustração vetorial de jogos de futebol de 202020 setembro 2024
Croácia e escócia na fase de grupos. ilustração vetorial de jogos de futebol de 202020 setembro 2024 -
 CELESTEELA Raid Counter Guide - 100 IVs, Weaknesses & More20 setembro 2024
CELESTEELA Raid Counter Guide - 100 IVs, Weaknesses & More20 setembro 2024 -
 Mewtwo png20 setembro 2024
Mewtwo png20 setembro 2024 -
 Jojo's Bizarre Adventure by Hirohiko Araki20 setembro 2024
Jojo's Bizarre Adventure by Hirohiko Araki20 setembro 2024 -
 Shantal Verdelho abre o jogo sobre cirurgia plástica depois da20 setembro 2024
Shantal Verdelho abre o jogo sobre cirurgia plástica depois da20 setembro 2024 -
 The Weeknd shares 'alternate world' remix of 'Sacrifice' with Swedish House Mafia20 setembro 2024
The Weeknd shares 'alternate world' remix of 'Sacrifice' with Swedish House Mafia20 setembro 2024
