Theory of Liquidity Preference Definition: History, Example, and
Por um escritor misterioso
Last updated 21 março 2025
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/liquiditypreference.asp-final-61b55e392c86409fb0b4cf0e2315bd40.jpg)
Liquidity preference theory concerns how stakeholders value cash relative to receiving interest over varying lengths of time.
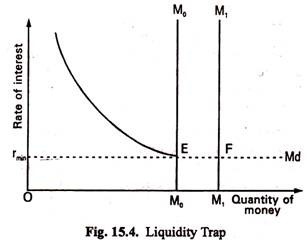
The Liquidity Preference Theory of Interest

Slide 0 CHAPTER 10 Aggregate Demand I In Chapter 10, you will learn… the IS curve, and its relation to the Keynesian cross the loanable funds model. - ppt download
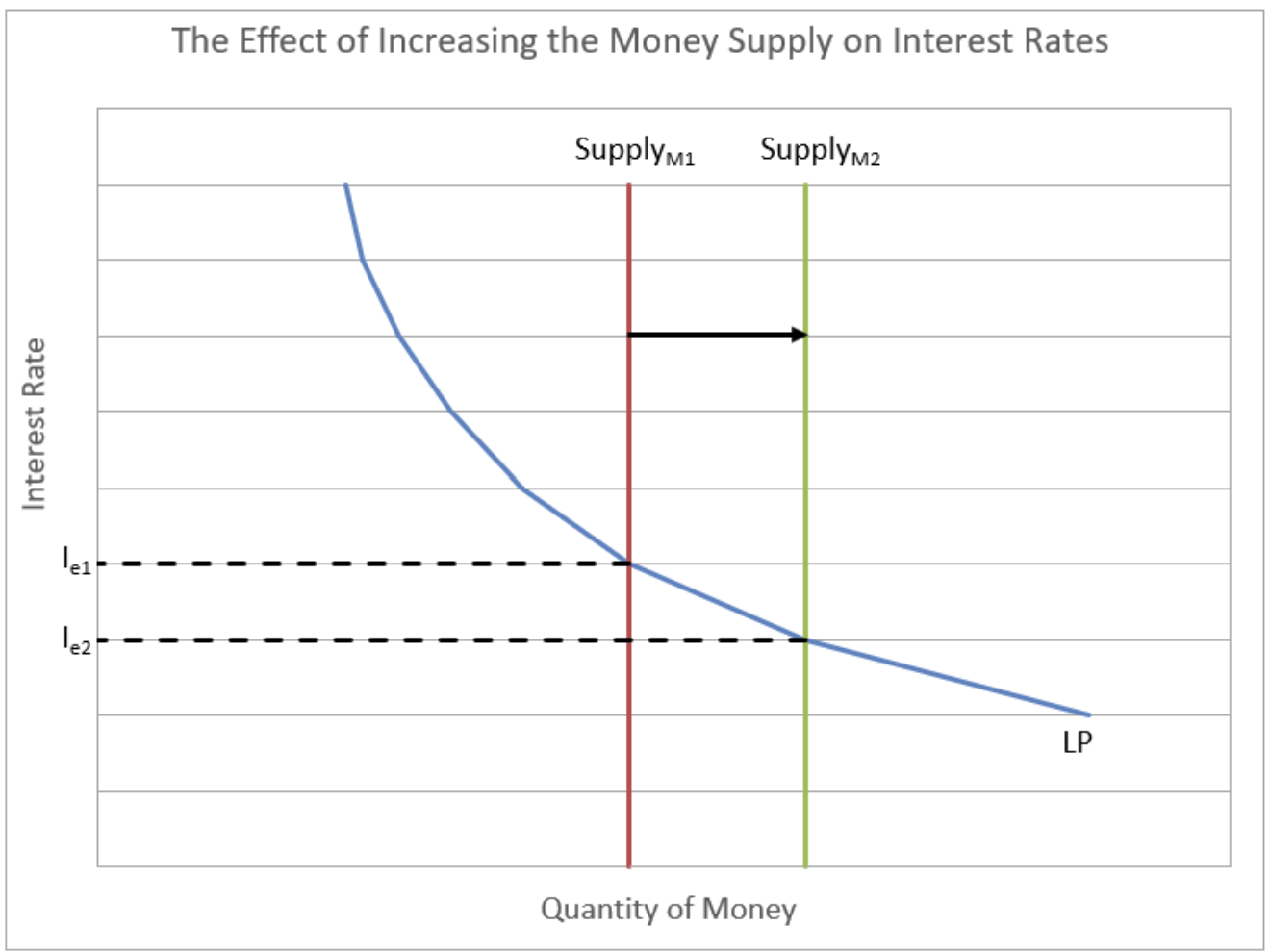
Definition of Liquidity Preference Model

SOLUTION: Keynesian liquidity preference theory and interest rate determination 1 - Studypool

PPT - Chapter VII: Money, assets, and interest rates PowerPoint Presentation - ID:51967
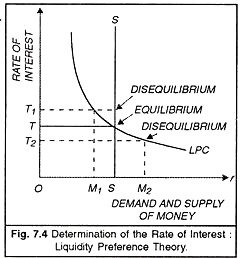
Keynes's Liquidity - Preference Theory of Interest Rate
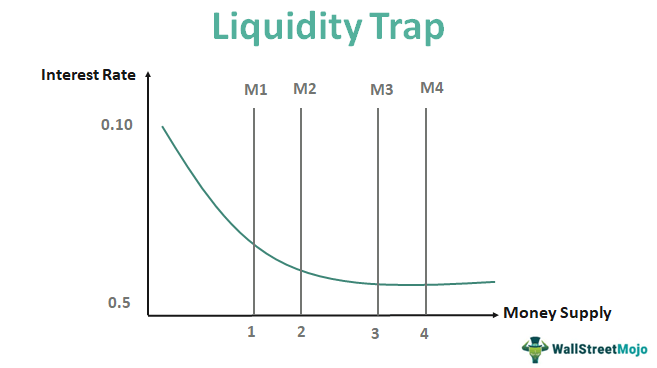
Liquidity Trap - What Is It, Solutions, Causes, Examples

PDF) Liquidity Preference Theory: A Comparison of William Baumol's and James Tobin's Propositions

Ch19
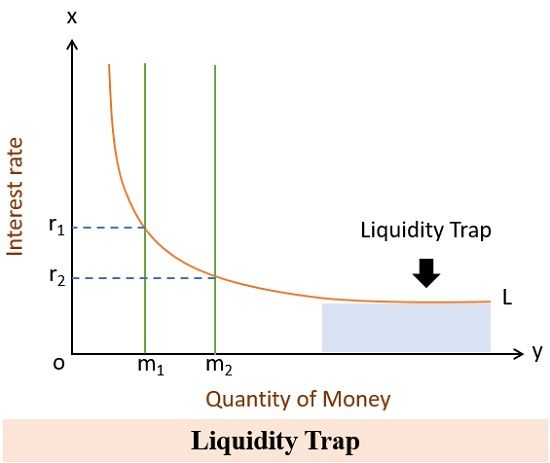
What is Liquidity Preference Theory? Definition, Diagram and Liquidity Trap- The Investors book
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/TheWayYouTitleYourUnitedStatesSavingsBondsCanHaveTaxConsequences-56ae67705f9b58b7d010097f.jpg)
Theory of Liquidity Preference Definition: History, Example, and How It Works

IS–LM model - Wikipedia

According to the liquidity preference theory of money, explain what happens when the interest rate is above the level that equates money demand with money supply. Provide a specific example to illustrate

The Keynesian System (II): Money, Interest, and Income - ppt download
Recomendado para você
-
 Press F to Pay Respects - Where Did It Come From? - Xfire21 março 2025
Press F to Pay Respects - Where Did It Come From? - Xfire21 março 2025 -
 What is the meaning and origin of 'Press F to pay respect'? - Quora21 março 2025
What is the meaning and origin of 'Press F to pay respect'? - Quora21 março 2025 -
 The Meaning and Origin of Press F to Pay Respects - VGKAMI21 março 2025
The Meaning and Origin of Press F to Pay Respects - VGKAMI21 março 2025 -
 Press F to Pay Respects: What Does F Mean Online?21 março 2025
Press F to Pay Respects: What Does F Mean Online?21 março 2025 -
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/financial-system_final-a9f735f765244e84829563e8a147abf2.jpg) Financial System: Definition, Types, and Market Components21 março 2025
Financial System: Definition, Types, and Market Components21 março 2025 -
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/Conglomerate_final_rev-1b7d5bca6813495cb54c86b5c98043f1.png) Conglomerate: Definition, Meaning, Creation, and Examples21 março 2025
Conglomerate: Definition, Meaning, Creation, and Examples21 março 2025 -
 What is a 'thot'? Meaning and origin explained21 março 2025
What is a 'thot'? Meaning and origin explained21 março 2025 -
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/export.asp-final-b6a4a3af93a5427e85efce9c6aba9cab.jpg) What Are Exports? Definition, Benefits, and Examples21 março 2025
What Are Exports? Definition, Benefits, and Examples21 março 2025 -
 Proptech: Its Definition and 28 Examples21 março 2025
Proptech: Its Definition and 28 Examples21 março 2025 -
 LeonButcher on X: Press F to pay respects on #CBLoL21 março 2025
LeonButcher on X: Press F to pay respects on #CBLoL21 março 2025
você pode gostar
-
 9 Neal Caffrey ideas neal caffrey, matt bomer, matt bomer white21 março 2025
9 Neal Caffrey ideas neal caffrey, matt bomer, matt bomer white21 março 2025 -
 Guia de Animais Exóticos/Saga Water 7, One Piece Wiki21 março 2025
Guia de Animais Exóticos/Saga Water 7, One Piece Wiki21 março 2025 -
Crunchyroll.pt - Chizuru 🥰❤ ⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀ ~✨ Anime: Rent-A21 março 2025
-
 Mobile wallpaper: Anime, Yellow Eyes, Brown Hair, Classroom Of The Elite, Kiyotaka Ayanokōji, 1380658 download the picture for free.21 março 2025
Mobile wallpaper: Anime, Yellow Eyes, Brown Hair, Classroom Of The Elite, Kiyotaka Ayanokōji, 1380658 download the picture for free.21 março 2025 -
 profile pic for girls Images • ❤️⃝✺͜͢͡➛͙ͥͥͥ⋆ͣ͟⋆ͫ🇷uhi✮͜͡👑✰࿐ (@ruhi__creation_) on ShareChat21 março 2025
profile pic for girls Images • ❤️⃝✺͜͢͡➛͙ͥͥͥ⋆ͣ͟⋆ͫ🇷uhi✮͜͡👑✰࿐ (@ruhi__creation_) on ShareChat21 março 2025 -
 Suppose a Kid from the Last Dungeon Boonies Moved to a Starter Town, Vol. 6 (light novel) (Tatoeba Last Dungeon Mae no Mura no Shounen ga Joban no Machi de Kurasu Youna21 março 2025
Suppose a Kid from the Last Dungeon Boonies Moved to a Starter Town, Vol. 6 (light novel) (Tatoeba Last Dungeon Mae no Mura no Shounen ga Joban no Machi de Kurasu Youna21 março 2025 -
 Delicioso salgado coreano! 3 receitas de salsichão21 março 2025
Delicioso salgado coreano! 3 receitas de salsichão21 março 2025 -
 Giant Hammer Mod On New Level - MODDED Getting Over It With Bennett Foddy21 março 2025
Giant Hammer Mod On New Level - MODDED Getting Over It With Bennett Foddy21 março 2025 -
 Spanish sin pena, erasing the stigma of non-fluency21 março 2025
Spanish sin pena, erasing the stigma of non-fluency21 março 2025 -
 Doors in Rockford - Entry, Storm, Screen, Patio Doors21 março 2025
Doors in Rockford - Entry, Storm, Screen, Patio Doors21 março 2025
